National Cancer Awareness Day: National Cancer Awareness Day is observed on November 7 in India. Every year, this day is observed to draw attention to the importance of the condition and to raise awareness about its early detection, treatment, and diagnosis.

National Cancer Awareness Day
According to WHO statistics, low- and middle-income nations account for about 70% of cancer-related fatalities. Because of factors like smoking, having a high body mass index, drinking, eating few fruits and vegetables, and not exercising enough, about one-third of deaths are caused by this disease. This disease has a sizable and growing financial impact.
Across the world, it is the leading cause of death, accounting for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020 and the most common were:
– breast (2.26 million cases);
– lung (2.21 million cases);
– colon and rectum (1.93 million cases);
– prostate (1.41 million cases);
– skin (non-melanoma) (1.20 million cases); and
– stomach (1.09 million cases).
In 2020, the most common causes of death were:
– lung (1.80 million deaths);
– colon and rectum (935 000 deaths);
– liver (830 000 deaths);
– stomach (769 000 deaths); and
– breast (685 000 deaths).
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), it is the second leading cause of death globally. In 2018, there were around 0.8 million deaths in India against 9.5 million globally. By 2040, the number of new cases is estimated to double in India.
National Cancer Awareness Day: History
National Cancer Awareness Day was first announced by the Union Health Minister Dr. Harsh Vardhan in September 2014. Therefore in 2014, the day was celebrated for the first time and focuses on the early detection and cure of this disease.
This day also coincides with the birth anniversary of the eminent French-Polish scientist Madame Curie who is known for her work in the field of radioactivity and has been the winner of the Nobel Prize twice.
India initiated a vital step in the fight against this lethal disease in 1975, with the initiation of the National Cancer Control Program, which was aimed to deliver cancer treatment amenities to the populace, after ten years the vision of this scheme was revised to pay attention on prompt detection and prevention of lethal disease.
In India, 13,24,413 new cases of lethal disease were diagnosed in the year 2020, and two-thirds of cases are diagnosed at an advanced stage, thus decreasing the chances of survival. Reports state that one woman loses her life due to cervical cancer every 8 minutes in India. Tobacco-related cancers account for 3,17,928 mortalities in men and women in 2018. Oral cavity and lungs account for over 25% deaths in males and breast and oral cavity cancers account for 25% in females. Around 70% of the factors that lead to this lethal disease are preventable which include chemical and atmospheric pollutants, poor eating habits, sedentary lifestyle, and infections.
On this health day, government motivates people to visit hospitals, Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) centers, and municipal clinics for free screening. Early diagnosis and treatment can detect malignancies in their earliest stages and better survival outcomes. Also, several activities have been formulated to improve research on the prevention, and early detection of this lethal disease.
Effective Ways To Prevent
Avoid Tobacco In All Forms
Yes, using any form of tobacco can up the risk of this lethal disease. Smoking has been associated with several types of this lethal disease, such as cancer of the lung, mouth, throat, larynx, pancreas, bladder, cervix, and kidney. While chewing tobacco has been linked to the oral cavity and pancreas. Even passive smoke might increase the risk of this lethal disease in lungs.
Refraining from tobacco or deciding to quit smoking is a crucial part of prevention. If you need support with quitting tobacco, ask your physician about the different types of smoking cessation products that are available and other effective strategies for quitting.
Eat A Wholesome And Varied Diet
Eating a balanced and healthy diet goes a long way in augmenting your health and well-being. Some of these guidelines can help avert the risk:
Have plenty of rainbow-colored fruits and vegetables and other plant-based foods like whole grains and beans. Eat leaner by choosing minimal amounts of high-calorie foods such as refined sugars and fat from animal sources.
Limit processed meats. Several pieces of evidence state that eating large servings of processed meat can gradually increase your risk of this lethal disease.
Follow a Mediterranean diet that comprises mainly plant-based food, whole grains, legumes, and nuts and a healthy source of fats can greatly lessen the risk of this deadly disease.
If you choose to drink alcohol, drink so in moderation. As long-term consumption of alcohol can increase the risk of this disease in breast, colon, lung, kidney, and liver.
Manage Weight/ Lead An Active Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy weight is one of the effective ways to reduce the risk of developing several types of cancer like breast, prostate, lung, colon, and kidney. While staying physically active also counts, as this may help one control weight and lower the risk of breast cancer and colon cancer. Aim to get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity a week or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity a week. The general goal is to include at least 30 minutes of physical activity in regular routine, and if you can stretch more, even better.
Protect From Sun Damage
Well, skin cancer is one of the most prevalent kinds of cancer and it is easily preventable. Follow these tips to mitigate the risk:
Stay away from the midday sun between 10.00A.M to 4.00 P.M, when the sun’s rays are strongest.
Stay in the shade while you’re outdoors as much as possible. Sunglasses and a broad-brimmed hat may also help.
Wear loose-fitting clothing that covers as much of your skin as possible. Go for dark colours, which reflect more UV rays than light-coloured dresses.
Never go out without applying sunscreen, even on cloudy days. Use a broad spectrum of sunscreen with at least 30 SPF.
Get vaccinated
Vaccines are available that offer protection against certain viral infections, talk to your healthcare provider about vaccination against:
Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B can up the risk of liver cancer. Doctors recommend certain people at high risk, to get the hepatitis B vaccine like those who are sexually active, but not in mutually monogamous relationships, people with STI, those who use IV drugs, men who have sex with men, and health care workers or public safety workers who may be exposed to infected blood or fluids.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV): HPV is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections that can lead to cervical and other genital cancers. It is highly recommended for girls and boys ages 11 and 12 to get the HPV vaccine to safeguard them against the risk of cancer later in life.
What is Cancer?
It is a large group of diseases that can start in almost any organ or tissue of the body when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, go beyond their usual boundaries to invade adjoining parts of the body and/or spread to other organs. The latter process is called metastasizing and is a major cause of death from cancer.
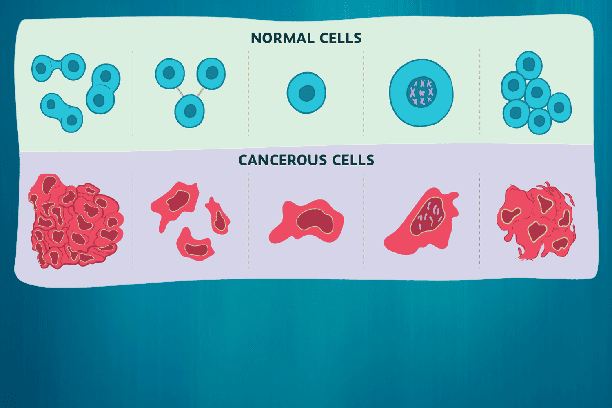
A neoplasm and malignant tumor are other common names for cancer. Lung, prostate, colorectal, stomach and liver cancer are the most common types of cancer in men, while breast, colorectal, lung, cervical and thyroid cancer are the most common among women.
What causes cancer?
Cancer arises from the transformation of normal cells into tumour cells in a multi-stage process that generally progresses from a pre-cancerous lesion to a malignant tumour. These changes are the result of the interaction between a person’s genetic factors and three categories of external agents, including:
physical carcinogens, such as ultraviolet and ionizing radiation;
chemical carcinogens, such as asbestos, components of tobacco smoke, aflatoxin (a food contaminant), and arsenic (a drinking water contaminant); and
biological carcinogens, such as infections from certain viruses, bacteria, or parasites.
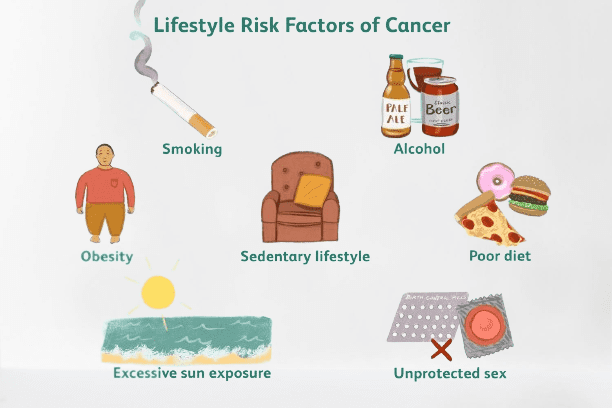
What are some of the risk factors for cancer?
Tobacco use, alcohol use, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity and air pollution are risk factors for cancer (and other noncommunicable diseases). Some chronic infections are risk factors for cancer. This is a particular issue in low- and middle-income countries. Approximately 13% of cancers diagnosed globally were attributed to carcinogenic infections, including Helicobacter pylori, human papillomavirus (HPV), hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and Epstein-Barr virus. Hepatitis B and C viruses and some types of HPV increase the risk for liver and cervical cancer, respectively. Infection with HIV substantially increases the risk of cancers such as cervical cancer.
How can we reduce the cancer burden?
Between 30% and 50% of cancers can currently be prevented by avoiding risk factors and implementing existing evidence-based prevention strategies.
The cancer burden can also be reduced through early detection of cancer and appropriate treatment and care of patients who develop cancer.
Many cancers have a high chance of cure if diagnosed early and treated appropriately.
How can we prevent cancer?
Cancer risk can be reduced by:
not using tobacco;
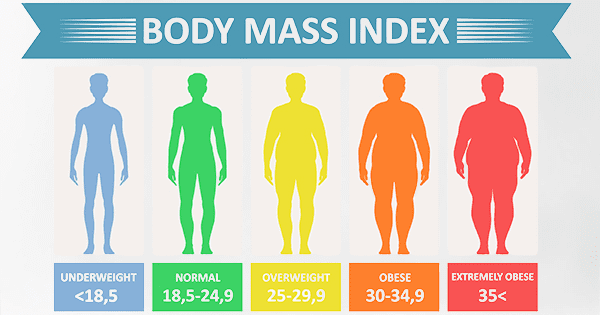
maintaining a healthy body weight (Know about Body Mass Index);
Use the BMI Calculator to know your healthy body weight.
eating a healthy diet, including fruit and vegetables;
doing physical activity on a regular basis;
avoiding harmful use of alcohol;
getting vaccinated against HPV and hepatitis B if you belong to a group for which vaccination is recommended;
avoiding ultraviolet radiation (which primarily results from exposure to the sun and artificial tanning devices);
ensuring safe and appropriate use of radiation in health care (for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes);
minimizing occupational exposure to ionizing radiation; and
reducing exposure to outdoor air pollution and indoor air pollution, including radon (a radioactive gas produced from the natural decay of uranium, which can accumulate in buildings — homes, schools and workplaces).
Early Detection of Cancer
Cancer deaths can be reduced if cases are detected and treated early. There are two components of early detection:
Early diagnosis
When identified early, cancer is more likely to respond to treatment and can result in a greater probability of survival and less morbidity, as well as less expensive treatment. Significant improvements can be made in the lives of cancer patients by detecting cancer early and avoiding delays in care.
Early diagnosis consists of three components:
Being aware of the symptoms of different forms of cancer and of the importance of seeking medical advice if you are concerned;
access to clinical evaluation and diagnostic services; and
timely referral to treatment services.
Early diagnosis of symptomatic cancers is relevant in all settings and the majority of cancers. Cancer programmes should be designed to reduce delays in, and barriers to, diagnosis, treatment and care.
Screening
Screening aims to identify individuals with findings suggestive of a specific cancer or pre-cancer before they have developed symptoms. When abnormalities are identified during screening, further tests to establish (or not) a diagnosis should follow, as should referral for treatment if needed.
Screening programmes are effective for some but not all cancer types and in general are far more complex and resource-intensive than early diagnosis as they require special equipment and dedicated personnel.
Patient selection for screening programmes is based on age and risk factors to avoid excessive false positive studies. Examples of screening methods are:
HPV testing for cervical cancer;
the PAP cytology test for cervical cancer;
visual inspection with acetic acid (VIA) for cervical cancer; and
mammography screening for breast cancer in settings with strong or relatively strong health systems.
Quality assurance is required for both screening and early diagnosis programmes.
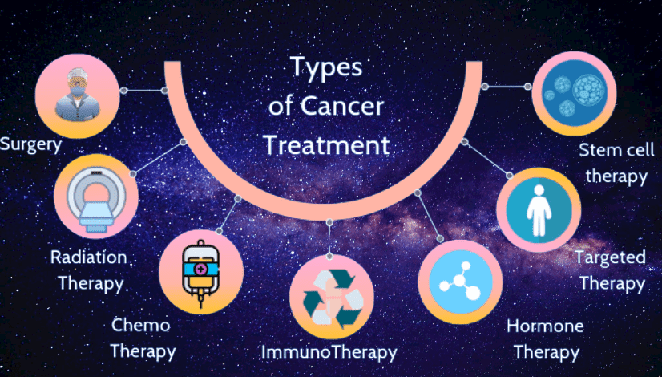
Cancer Treatments
A correct diagnosis is essential for appropriate and effective treatment because every type requires a specific treatment regimen. Treatment usually includes radiotherapy, chemotherapy and/or surgery. Determining the goals of treatment is an important first step. The primary goal is generally to cure or to considerably prolong life. Improving the patient’s quality of life is also an important goal. This can be achieved by support for the patient’s physical, psychosocial and spiritual well-being and palliative care in terminal stages.
Some of the most common types, such as breast, cervical, oral and colorectal have high cure rates when detected early and treated according to best practices. Some types, such as testicular seminoma and different types of leukemia and lymphoma in children, also have high cure rates if appropriate treatment is provided, even when cancerous cells are present in other areas of the body.
World Cancer Day
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) was created in 1965 by a resolution of the World Health Assembly, as the specialized cancer agency of the World Health Organization.

World Cancer Day is an international day marked on 4 February to raise awareness of this lethal disease and to encourage its prevention, detection, and treatment. This day is led by the (UICC) to support the goals of the World Cancer Declaration, written in 2008. The primary goal of this global Day is to significantly reduce illness and death caused by this disease. The day is observed by the United Nations.
The Day was established on 4 February 2000 at the World Cancer Summit Against Cancer for the New Millennium, which was held in Paris.
It causes almost 459 000 deaths every year in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Over the past five years, there were around 1.6 million cases in the Region, making it a continuous burden that exerts tremendous physical, emotional and financial strain on individuals, families and communities. Almost 734 000 individuals are diagnosed with this disease every year and in 2040 it is predicted that the number of people being diagnosed will be about 50% higher.
World Cancer Day aims to promote awareness on cancer as a public health issue and to strengthen actions towards improving access to quality care, screening, early detection, treatment and palliative care. This year’s theme is “close the care gap” which is about understanding the inequities in care and taking actions to make the necessary progress to address them.
It is the second leading cause of death worldwide, representing nearly 1 in 6 deaths globally. In WHO’s Eastern Mediterranean Region, most cases are diagnosed at a late stage when treatments are less effective which results in poorer outcomes for patients. Modelled estimates indicate that by 2030 the Region will have the highest increase burden among all six WHO regions. In spite of positive developments in some countries of the Region, the prevention and control in countries of the Region remained at an early stage of development, with limited strategic direction.
IMPORTANT FACTS
| IMPORTANT/UNKNOWN FACTS | |
| What is Cancer? | It is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body |
| Signs | Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements |
| Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of deaths | |
| Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive alcohol consumption | |
| Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants | |
| Approximately 5–10% are due to inherited genetic defects. | |
| How to avoid the risk? | The risk of developing certain types of this disease can be reduced by not smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol intake, eating plenty of vegetables, fruits, and whole grains, vaccination against certain infectious diseases, limiting consumption of processed meat and red meat, and limiting exposure to direct sunlight. |
| In 2015, about 90.5 million people worldwide had this disease. | |
| In 2019, annual cases grew by 23.6 million people and there were 10 million deaths worldwide | |
| Common in Male | The most common types in males are lung, prostate, colorectal and stomach |
| Common in Female | In females, the most common types are breast, colorectal, lung and cervical. |
| Tobacco smoke, for example, causes 90% of lung cancer | |
| Tobacco also causes this disease in the larynx, head, neck, stomach, bladder, kidney, esophagus and pancreas. | |
| Tobacco is responsible for about one in five deaths worldwide and about one in three in the developed world | |
| In Western Europe, 10% in males and 3% of in females are attributed to alcohol exposure, especially liver and digestive tract types | |
| Diet, physical inactivity, and obesity are related to up to 30–35% of deaths | |
| In the United States, excess body weight is associated with the development of many types of this fatal disease and is a factor in 14–20% of deaths | |
| A UK study including data on over 5 million people showed higher body mass index to be related to at least 10 types of this disease and responsible for around 12,000 cases each year in that country. | |
| A high-salt diet is linked to gastric cancer | |
| Aflatoxin B1, a frequent food contaminant, causes liver cancer | |
| Betel nut chewing can cause oral cancer | |
| gastric cancer is more common in Japan due to its high-salt diet | |
| Worldwide, approximately 18% of deaths related to this fatal disease are related to infectious diseases | |
| Radiation exposure such as ultraviolet radiation and radioactive material is a risk factor for this disease. | |
| The word comes from the Latin for ‘crab’ – just like the zodiac sign. Early doctors, when describing certain tumors which had veins or extensions from the main body, called them crab-like, or ‘cancerous’. | |
| The left breast is 5 – 10% more likely to develop this disease than the right breast. The left side of the body is also 10% more prone to melanoma. | |
| The disease in Childhood account for 1 percent of all new diagnoses. In 2018, about 15,590 children and teens ages (ages 0-19) were diagnosed with this disease. Although uncommon, it is the leading cause of death by disease in children | |
| About 67% of Americans diagnosed with this disease survive five or more years after their diagnoses | |
| It is not considered as an infectious or communicable disease. It cannot be transmitted from one person to another through touching, kissing, having sex, sharing meals or breathing the same air. With a few rare exceptions, such as organ transplant and mother-to-fetus transmission, in most cases the immune system will recognize foreign cells (from another person) and destroy them. | |
| All Tumors Are Not Cancerous | |
| It Leads to Hair Loss. While the disease itself doesn’t typically cause hair loss, the treatment does. Chemotherapy and radiation are used to kill rapidly growing cells in the body, but they also kill healthy cells in the process. Other side effects of Chemotherapy include a high risk of infections, mouth sores and diarrhoea. | |
| Hair follicles are one of the fastest growing cells in the body. The hair follicles of a healthy individual divide every 23 to 72 hours. But if the patient is undergoing chemotherapy, the treatment acts against the hair follicles, causing hair to shed. Some chemotherapy drugs not only affect the hair on the head, but they can also cause loss of eyebrows and eyelashes, pubic hair, and hair on your legs, arms, or underarms. | |
| Every Three Minutes, Someone in the U.S. Is Diagnosed With Leukemia, Lymphoma or Myeloma | |
| And every nine minutes, someone dies from this disease related to blood. | |